Products You May Like
A brand new malware is bypassing an Android 13 safety measure that restricts permissions to apps downloaded out of the authentic Google Play Retailer.
A brand new report from ThreatFabric, a fraud safety firm, exposes SecuriDropper malware, which is able to bypassing Android 13 restricted settings. The malware makes Android contemplate the set up as coming from the Google Play Retailer, although in actuality it isn’t.
It’s extremely really useful for organizations to make use of Cellular Machine Administration options and strategies to allow extra management on workers’ Android units and to limit putting in apps on their units by utilizing an inventory of accredited functions and forbidding some other.
Bounce to:
What are Android 13’s restricted settings?
Android 13 launched a brand new safety characteristic known as restricted settings. This new characteristic prevents sideloaded functions (i.e., downloaded out of the Google Play Retailer) from instantly requesting accessibility settings and notification listener entry — two options which can be typically abused by malware in response to ThreatFabric’s researchers.
On Android programs, functions downloaded from the authentic Google Play Retailer aren’t topic to the identical course of as these not originating from it. The principle motive why is that functions which have made it efficiently to the Google Play Retailer have offered extra data and visibility and have handed totally different safety exams to make sure they don’t comprise malware functionalities. Due to this fact, functions from the Google Play Retailer aren’t involved by the restricted settings characteristic.
Purposes downloaded from the Play Google Retailer use a particular set up technique — a “session-based” bundle installer — that isn’t usually utilized by sideloaded functions.
Meet SecuriDropper malware
The SecuriDropper malware makes use of the identical set up technique as authentic software program from the authentic Google Play Retailer. After being executed by the unsuspecting consumer, the malware requests two key permissions: Learn & Write Exterior Storage and Set up & Delete Packages.
As soon as permissions are given, the malware checks if it already exists on the machine; if it does, the malware runs, and if it doesn’t, the malware exhibits the consumer a message telling them one thing went mistaken and the consumer must click on a reinstall button. The message is totally different primarily based on the machine’s location and language configured.
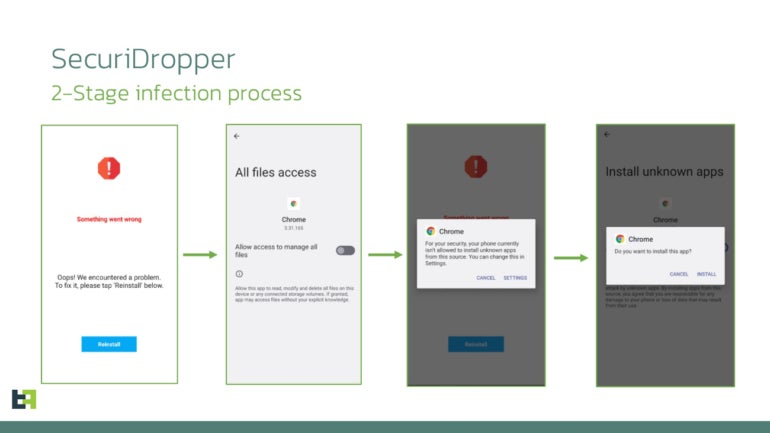
When accomplished, the session-based set up begins, and the consumer is requested for permission to allow the Accessibility Service, which turns into doable because of the bypass of the restricted settings characteristic (Determine A).
Determine A
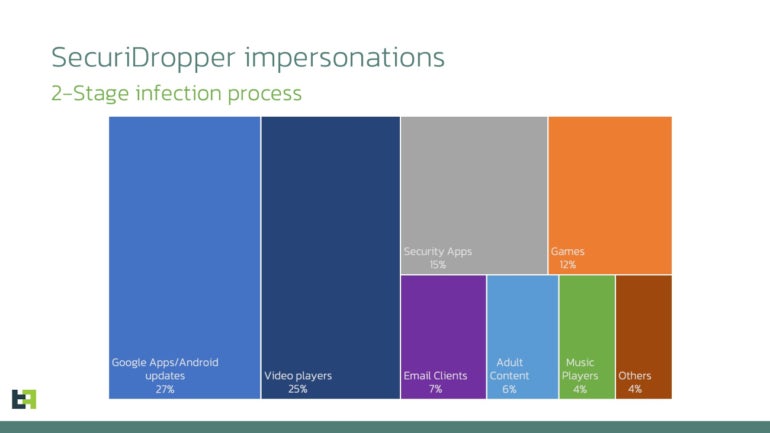
The malware has been noticed disguising itself as varied Android functions akin to Google Apps or Android updates (27%), video gamers (25%), safety functions (15%) or video games (12%), adopted by e-mail shoppers, grownup content material, music gamers and different apps (Determine B).
Determine B
SecuriDropper’s varied ultimate payloads
Any sort of malicious code might be dropped and put in by SecuriDropper, because the malware’s ultimate purpose is to put in different malware on contaminated units. ThreatFabric noticed two campaigns utilizing SecuriDropper.
The primary one is an assault marketing campaign delivering SpyNote, a malware with distant administration software options. The malicious payload was being distributed via phishing web sites and deployed by SecuriDropper. The SpyNote malware, which is ready to seize delicate data on the machine, in addition to steal SMS and name logs and take screenshots, completely wants permissions that might be unavailable because of Android’s restricted settings. Its set up through SecuriDropper permits the SpyNote malware to maintain infecting units, even on Android 13, without having to alter its code.
In one other assault marketing campaign, SecuriDropper was noticed putting in the ERMAC banking trojan. The malware was deployed through Discord, a communication software beforehand used primarily by avid gamers however more and more utilized by different communities, together with company entities.
Extra malware will use this method
Completely different malware households will use this method sooner or later. One service that’s already utilizing this method is Zombinder.
As reported by ThreatFabric, the DarkNet platform Zombinder began promoting for its new model that bypasses Android 13 restricted settings. The Zombinder service permits an attacker to efficiently bind a authentic utility with malware. When the an infection is finished, the authentic utility runs usually, whereas the malware is being executed within the background, unnoticed.
Zombinder additionally sells builders with the Android 13 restrictions bypass functionality. The builders from Zombinder are software program able to dropping malware on an contaminated system (aka dropper), offered at $1,000 USD.
As written by ThreatFabric, “the emergence of services like Zombinder are indications of a booming market in cybercrime, offering builders and tools for evading Android 13’s defenses. It is a testament to the resourcefulness of those seeking to exploit security vulnerabilities for their gain.”
Disclosure: I work for Development Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.
